Squint,Lid Disorder & Orhtoptics
About Squint,Lid Disorder & Orhtoptics
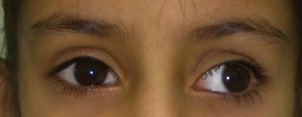
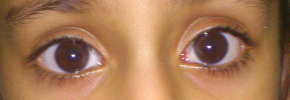
What is a Squint?
Strabismus, Squint or crossed eyes refers to a condition in which both the eyes do not align with each other while focussing on an object.
If it is present during a large part of childhood, it may result in patient having amblyopia (Lazy eye/decrease vision) with loss of depth perception. In children it can be due to uncorrected refractive error, prematurity, birth trauma, trauma, infection, associated family history.
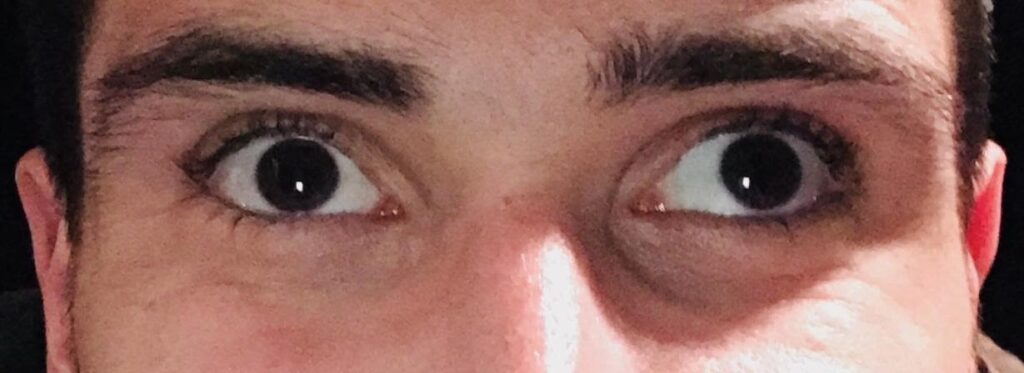
Types and Treatments for a Squint?
Treatment depends on the type of strabismus and the underlying cause. Treatment may include glasses, surgery and simultaneous management for amblyopia in the form of patching. Earlier the treatment better is the depth of perception and stereopsis. Strabismus in a child must be taken care of at the earliest and the specialist to be concerned for the same as sometimes strabismus may be the presenting sign of underlying disease like retinoblastoma. So my message to the parents is don’t get scared of glasses or squint in your child as it may have worse impact on his/her quality of life….
In adults squint may be associated with decreased vision or suppression if the squint is from childhood. Acquired squint in adults may be associated with double vision or diplopia. It can be due to refractive error (commonly myopia), trauma, infection, diabetes, fever, tumour or any intracranial pathology. Proper workup (metabolic and neuroimaging) is mandatory as squint can be the earliest manifestation of underlying disorder. Surgery in adults is done to align the eyes, to relieve patient of diplopia and to alleviate any abnormal head posture if associated. Realistic expectations have to be discussed with patients before surgery especially in cases of neuroparalytic strabismus.
Psychological Impacts and Surgical Options for a Squint?
Treatment depends on the type of strabismus and the underlying cause. Treatment may include glasses, surgery and simultaneous management for amblyopia in the form of patching. Earlier the treatment better is the depth of perception and stereopsis. Strabismus in a child must be taken care of at the earliest and the specialist to be concerned for the same as sometimes strabismus may be the presenting sign of underlying disease like retinoblastoma. So my message to the parents is don’t get scared of glasses or squint in your child as it may have worse impact on his/her quality of life….
In adults squint may be associated with decreased vision or suppression if the squint is from childhood. Acquired squint in adults may be associated with double vision or diplopia. It can be due to refractive error (commonly myopia), trauma, infection, diabetes, fever, tumour or any intracranial pathology. Proper workup (metabolic and neuroimaging) is mandatory as squint can be the earliest manifestation of underlying disorder. Surgery in adults is done to align the eyes, to relieve patient of diplopia and to alleviate any abnormal head posture if associated. Realistic expectations have to be discussed with patients before surgery especially in cases of neuroparalytic strabismus.