Test Tube Baby (IVF / ICSI)
Test Tube Baby (IVF/ ICSI)
What is IVF ?
The steps of IVF are:
- Stimulation of Egg Maturation
- Egg Retrieval
- Fertilization
- Embryo Transfer
Preparing for an IVF Cycle
- Before the first cycle a physician will do a semen analysis for the male partner and a trial or mock embryo transfer. IVF is generally preceded by the use of ovulation-stimulating drugs to increase the number of mature eggs that can be retrieved.
- The process of IVF usually includes Ovulation Induction, Egg Retrieval and Embryo Transfer.
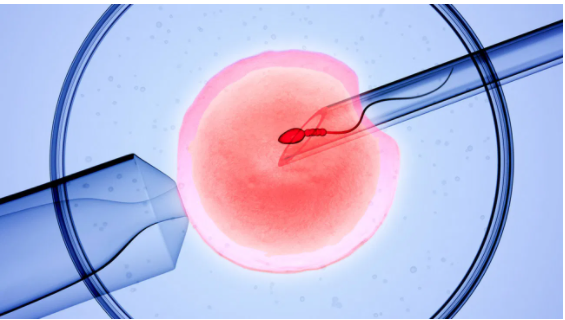
What is Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)?
- Before a man’s sperm can fertilize a woman’s egg, the head of the sperm must attach to the outside of the egg. Once attached, the sperm pushes through the outer layer to the inside of the egg (cytoplasm), where fertilization takes place. Sometimes the sperm cannot penetrate the outer layer, for a variety of reasons. The egg’s outer layer may be thick or hard to penetrate or the sperm may be unable to swim. In these cases, a procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can be done along with in vitro fertilization (IVF) to help fertilize the egg. During ICSI, a single sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm the egg.
How does ICSI work?
There are two ways that an egg may be fertilized by IVF: traditional and ICSI. In traditional IVF, 50,000 or more swimming sperm are placed next to the egg in a laboratory dish. Fertilization occurs when one of the sperm enters into the cytoplasm of the egg. In the ICSI process, a tiny needle, called a micropipette, is used to inject a single sperm into the center of the egg. With either traditional IVF or ICSI, once fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg (now called an embryo) grows in a laboratory for 1 to 5 days before it is transferred to the woman’s uterus (womb).
Why would I need ICSI?
- ICSI helps to overcome fertility problems, such as:
- The male partner produces too few sperm to do artificial insemination (intrauterine insemination [IUI]) or IVF.
- The sperm may not move in a normal fashion.
- The sperm may have trouble attaching to the egg.
- A blockage in the male reproductive tract may keep sperm from getting out.
- Eggs have not fertilized by traditional IVF, regardless of the condition of the sperm.
- In vitro matured eggs are being used.
- Previously frozen eggs are being used.
Other Services
Embryo Freezing
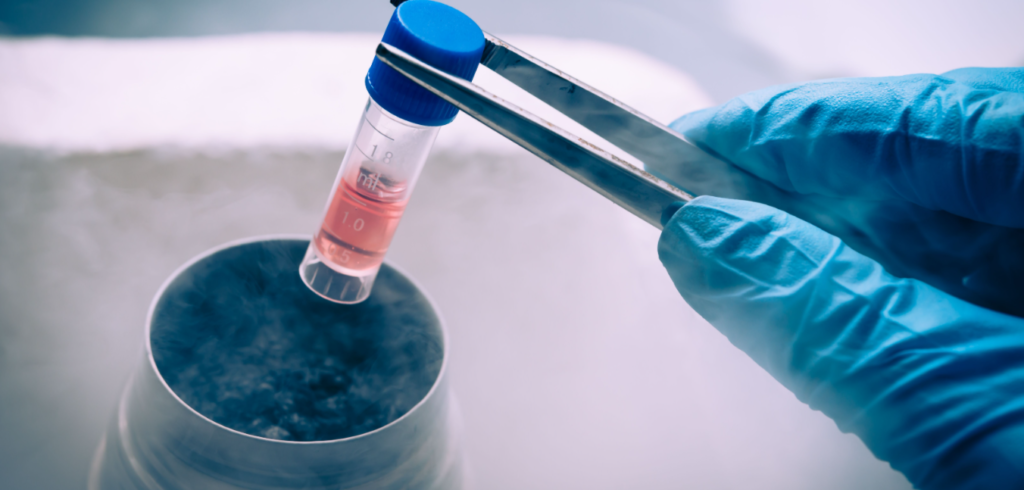
Embryo freezing is a procedure that allows people to store embryos for later use. … A doctor can then transfer the embryo to the womb, or uterus. If the treatment is successful, the embryo will develop. Fertilization often results in more than one embryo, and the doctor can freeze and preserve the remaining embryos
Donor Program
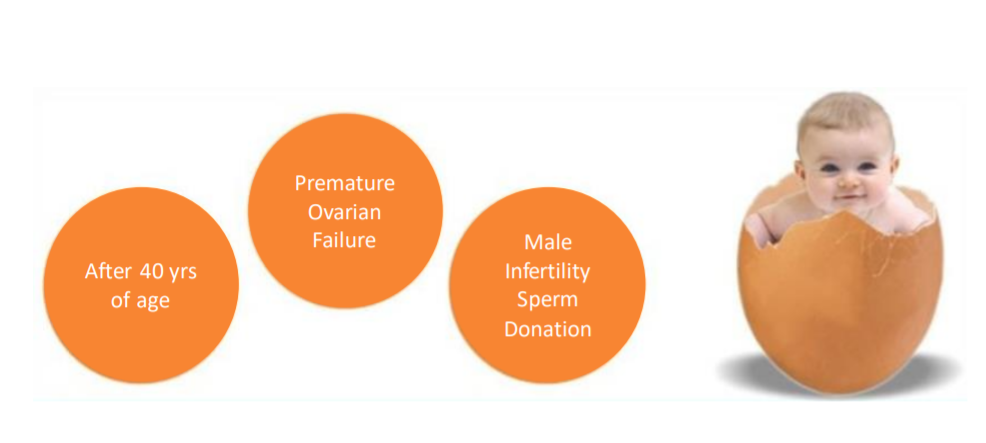
WHO REQUIRE EGG DONATION?
- If a woman has no ovaries (either cogenitally absent or removed due to any surgery).
- Women having very low quality of ovarian reserve, may be due to age or can be some unexplained reason.
- A previous history of IVF failures.
- Premature Ovarian failure (where menopause has started much earliar, before 40).
- Genetically transmitted disease that could be passed on to your child.
Vitrification

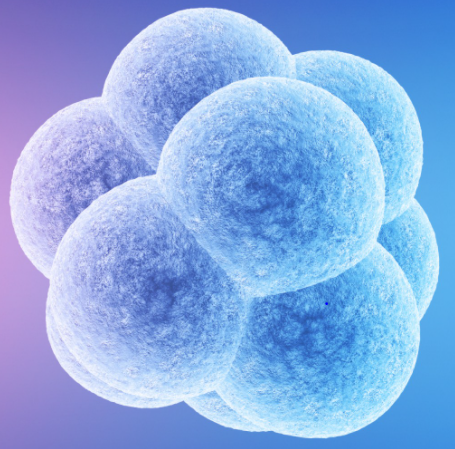
Blastocyst Transfer
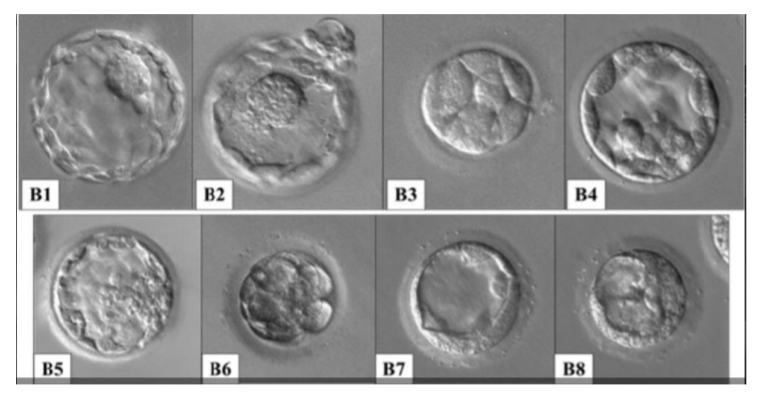
- The pronuclear stage on the first day (fertilised egg)
- The two to four-cell stage on the second day
- The eight-cell stage on the third day
- The morula stage on the fourth day and
- The blastocyst stage on the fifth day

